How Blocking Robots Allows Your Best Content to Shine
Robots are often the stuff of science fiction. But when it comes to SEO, robots play a critical role in how search engines understand and index your website.
Many business owners don’t know this, but all websites contain something called a sitemap that helps search engines navigate and understand the website’s content. A part of that sitemap is a small text file called a robots.txt file. This file is used strategically to prevent search engines crawlers from either accessing specific pages or even your entire site, depending on the circumstances.
So why is blocking robots so critical when it comes to maximizing your crawl budget and boosting the visibility of your best content? Keep reading to find out!
What Is a Robots.txt File?
When we speak of blocking robots, it might evoke mental images of battling giant steel beings. In reality, it’s a strategy that webmasters and SEO experts have been deploying for decades.
In the world of SEO, robots are any type of “bot” that visit webpages. You’re probably most familiar with search engine crawlers like Googlebot, which “crawl” around the web to help search engines like Google sort through and rank billions of pages of content.
That’s where robots.txt comes in. Robots.txt is a part of your sitemap, a file listing every page on a website. These files are essentially a common language that websites use to communicate with web crawlers to help them understand your website content.
Search engine crawlers utilize these files to sort through, index, and catalog your website content.
If you have a robots.txt file, it can typically be found in the root of your website domain by adding /robots.txt after your domain. For example, www.example.com/robots.txt.
When you use your robots.txt.file for blocking robots, it serves as a kind of digital invisibility cloak that either disallows crawlers entirely or restricts their access to specific pages of your site.
Robots.txt vs. Meta Noindex Tags
If your goal is to prevent certain webpages from appearing in search engine results altogether, you want to use a meta noindex tag, or develop a page with password protection.
The reason for this is that robots.txt files don’t actually tell search engines not to index your content — it’s simply telling them not to crawl it.
Additionally, if external sites contain backlinks to pages you’ve opted to hide with your robots.txt file, search engines like Google are still capable of indexing that page. So it’s not always 100% foolproof.
Your best bet if you want to exclude a page from search engines is to use the noindex meta tag.
When to Block vs. When Not to Block
Not all robots come in peace. Although a robots.txt file can try to force bots to follow its commands, some malicious bots will ignore it entirely.
Does that mean you should block all bots from your site? Not necessarily. Blocking robots entirely can actually be detrimental to your website’s search engine visibility.
However, there are three common cases where blocking bots can work to your advantage.
1. Maximize Your Crawl Budget
Blocking robots from areas of your site that don’t need indexing can help optimize search engine crawlers’ resources. The last thing you want is for a crawler to miss out an essential piece of content because it was wasting time on an old, unused webpage.
Part of any successful content promotion plan is to highlight content that you do want to get seen. To achieve this, you can block robots from lower priority content such as duplicates or archived sections of your site.
2. Optimize Site Load Speed and Bandwidth
Some bots consume a lot of server resources, which place an incredible load on your server and slow down the site for actual visitors. Especially if your website has a large amount of content or pages that experience frequent crawling, a slowdown in load speed can amplify into a serious issue.
Blocking robots from pages with large media files that take considerable time to load or highly dynamic pages can reduce unnecessary strain on your server and improve your user experience.
3. Hide Irrelevant Information From the Public
When it comes to content on your site being found by search crawlers, there are some pages that may be pointless to include in search results. This might be information meant only for employees, shopping carts for e-commerce stores, or things like thank-you pages.
Giving these pages a piece of your valuable search real estate can detract from your content that you want to get seen — it’s usually easier to hide it.
However, if we’re talking about highly sensitive information, it’s generally safer to use a noindex tag, since robots don’t always follow the directives laid out in robot.txt files.
One thing to keep in mind is not all websites need a robots.txt file. If you don’t have an issue with crawlers having free rein of your content, then you might opt not to bother with adding one at all.
How to Configure Robots.txt
Don’t worry — setting up a robot.txt file is pretty straightforward.
Some content management systems (such as WordPress) will automatically create a robots.txt file for your site. You can also create and edit robot.txt files with popular SEO plugins like Yoast, or have an experienced webmaster handle it for you.
If you want to be able to edit your robots.txt file and give more specific directives, you’ll need to create a physical file that lives on your server. This process is a bit more involved, but generally, there are three steps:
- Choose a text editor: You can use any basic text editor such as Notepad or TextEdit.
- Draft your directives: This essentially hides certain web pages from web crawlers by preventing them from accessing the “private” directory on your site.
- Save and upload: Lastly, save the file as “robots.txt” and place it in your website’s root directory.
What to Include in Your Robots.txt File
When configuring your robots.txt file, you can choose to block all bots and crawlers from accessing your site or block specific crawlers.
To understand how to block search engine bots and crawlers you need to understand a few key terms:
- User agents: These “names” are what bots use to identify themselves. If you want to block specific bots, simply insert their user-agent name in the robots.txt file.
- Allow and Disallow: This indicates specific pages that you want to block bots from crawling.
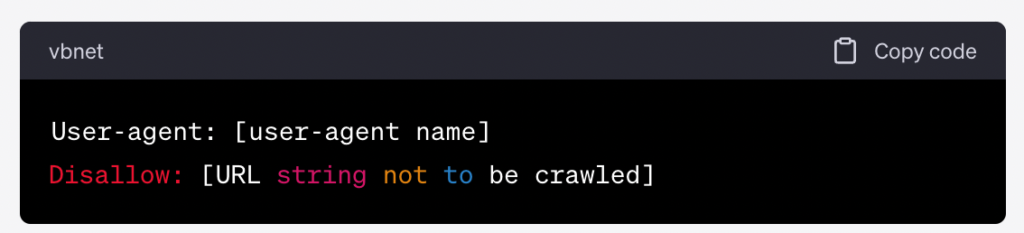
Let’s say you want to block all search engine crawlers from accessing your website. The chances of this are pretty unlikely, but it does come in handy when you’re in the process of editing or developing a new website.
To do this, you would add the user-agent name “*” and then the disallow directive to your robots.txt file:

Now, let’s say you want to block bots from certain search engines such as Google, but not Bing or Yahoo. You can include the user-agent name for Google Crawlers by using the command “Googlebot/Disallow” like in the example below:

Best Practices for Using Robots.txt
Blocking robots is a delicate dance between ensuring your site’s key content is visible to search engines and hiding content that you don’t want search engines to rank.
Here are some best practices to ensure that you protect your site without hiding essential content:
- Be specific: Instead of blocking large chunks of your website, be precise about which web pages or directories you block. Blocking specific URLs can help maintain search optimization and block pages with sensitive information, but one wrong move and you risk hiding some of your best content by mistake. Working with an SEO partner that understands technical SEO is the best way to ensure that search engines can crawl and index your website without any issues.
- Test your directives: Google Search Console is your best friend when it comes to blocking robots and managing robots.txt files. Google’s Robot Testing Tool (robots.txt Tester) allows you to test your robots.txt file to make sure it works as intended. You can also check specific URLs to see if they are allowed or disallowed by your robot.txt directives, as well as edit your robots.txt directly before making changes on your live site.
- Update your robots.txt file regularly: As your website content grows and evolves, make sure to update your sitemap and robots.txt file regularly to reflect key changes. Again, Google Search Console provides an easy way to do this if your site isn’t built on a CMS like WordPress that generates a robots.txt file automatically.
- Avoid blocking key content: When specifying which parts of your site you want to hide from search engines, double check that you aren’t inadvertently blocking JS, CSS, or image files that are crucial for rendering your website correctly. You don’t want to lose visitors due to something as small as a key infographic or image that won’t load properly.
Leave Your SEO Strategy to the Pros
Navigating the complexities of robots.txt and other SEO tools can be challenging for business owners. From developing high-quality content to protecting user privacy and maximizing crawler resources, it can all feel overwhelming at times.
That’s where an SEO agency comes in. A powerful SEO strategy supported by a sitemap and robots.txt file that highlight your top content is a surefire way to drive more traffic to the right places.
Reach out to us today for a technical audit and fully managed content services. We’ll help you showcase the best of what your site has to offer.







